Hyundai Elantra: ABS(Anti-Lock Brake System) / Description and operation
Hyundai Elantra (CN7) 2021-2025 Service Manual / Brake System / ABS(Anti-Lock Brake System) / Description and operation
| Description |
This specification applies to HCU(Hydraulic Control Unit) and ECU(Electronic Control Unit) of the HECU.(Hydraulic and Electronic Control Unit)
This specification is for the wiring design and installation of ABS/ESP ECU.
This unit has the functions as follows.
| – | Input of signal from Pressure sensor, Steering angle sensor, Yaw & Lateral G sensor, the wheel speed sensors attached to each wheel. |
| – | Control of braking force / traction force / yaw moment. |
| – | Failsafe function. |
| – | Self diagnosis function. |
| – | Interface with the external diagnosis tester. |
Installation position : engine compartment
| – | Brake tube length from Master cylinder port to HECU inlet port should be max. 1m |
| – | The position should not be close to the engine block and not lower than the wheel. |
Operation
The ECU shall be put into operation by switching on the operating voltage (IGN).
On completion of the initialization phase, the ECU shall be ready for operation.
In the operating condition, the ECU shall be ready, within the specified limits (voltage and temperature), to process the signals offered by the various sensors and switches in accordance with the control algorithm defined by the software and to control the hydraulic and electrical actuators.
Wheel Sensor Signal Processing
The ECU shall receive wheel speed signal from the four active wheel sensors.
The wheel signals are converted to voltage signal by the signal conditioning circuit after receiving current signal from active wheel sensors and given as input to the MCU.
Solenoid Valve Control
When one side of the valve coil is connected to the positive voltage that is provided through the valve relay and the other side is connected to the ground by the semiconductor circuit, the solenoid valve goes into operation.
The electrical function of the coils are always monitored by the valve test pulse under normal operation conditions.
Voltage Limits
| – | Overvoltage When overvoltage is detected(above 16.9 V), the ECU switches off the valve relay and shuts down the system. When voltage is returned to operating range, the system goes back to the normal condition after the initialization phase. |
| – | Undervoltage In the event of undervoltage(below 9.4 V), ABS control shall be inhibited and the warning lamp shall be turned on. When voltage is returned to operating range, the warning lamp is switched off and ECU returns to normal operating mode. |
Pump Motor Checking
The ECU performs a pump motor test at a speed once after IGN is switched on.
Diagnostic Interface
Failures detected by the ECU are encoded on the ECU, stored in a EEPROM and read out by diagnostic equipment when the ignition switch is turned on.
The diagnosis interface can also be used for testing the ECU during production of the ECU and for actuating the HCU in the test line of manufactories (Air-bleeding line or Roll and Brake Test line).
Warning Lamp Module
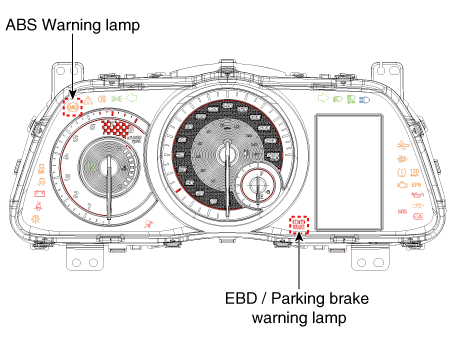
| 1. | ABS Warning Lamp module The active ABS warning lamp module indicates the self-test and failure status of the ABS. The ABS warning lamp shall be on :
|
| 2. | PARKING/EBD warning lamp module The active EBD warning lamp module indicates the self-test and failure status of the EBD. However, in case the Parking Brake Switch is turned on, the EBD warning lamp is always turned on regardless of EBD functions. The EBD warning lamp shall be on :
|
| ABS Control |
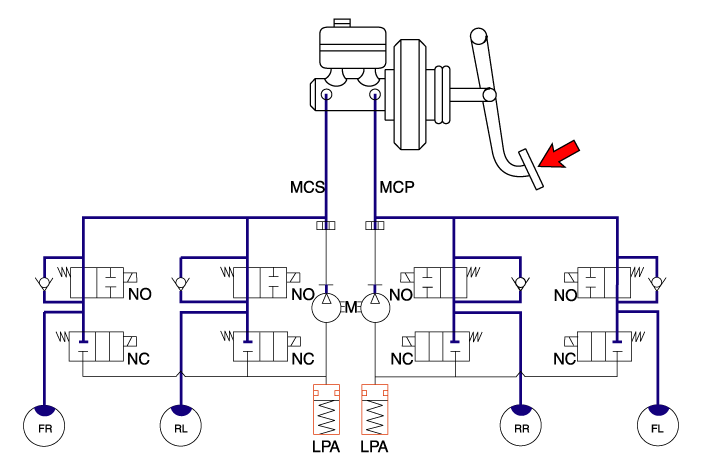
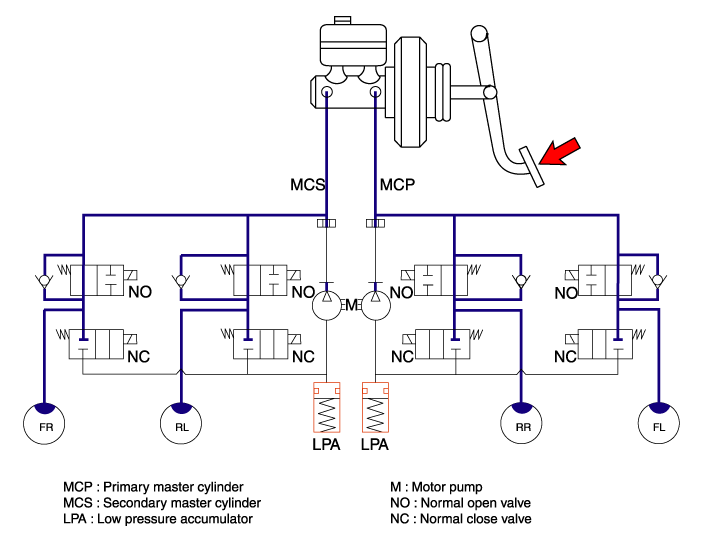
| 1. | NORMAL BRAKING without ABS Under the normal braking, voltage is not supplied to solenoid valve, inlet valve is opened and outlet valve is closed. When the brake is depressed, brake fluid is supplied to the wheel cylinder via solenoid valve to activate the brake.When the brake is released, brake fluid is back to the master cylinder via inlet valve and check valve.
|
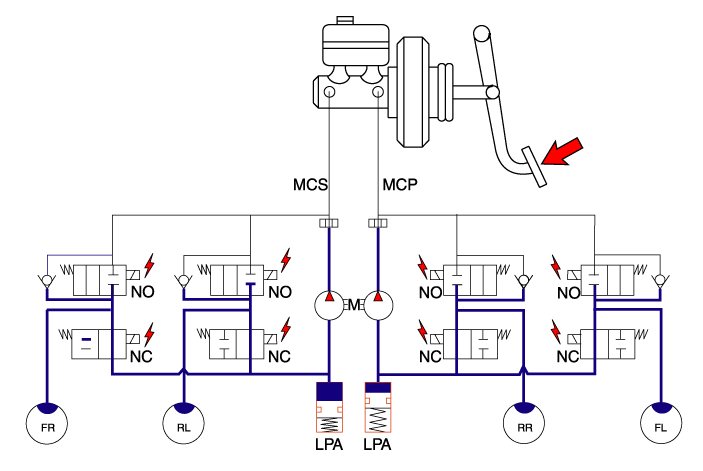
| 2. | Dump Mode Under the emergency braking, if the wheels start to lock up, HECU sends a signal to the solenoid valve to decrease the brake fluid, then voltage is supplied to each solenoid. At this time inlet valve is closed and brake fluid is blocked from the master cylinder. Conversely outlet valve is opened and brake fluid passes through wheel cylinder to reservoir, resulting in pressure decrease.
|
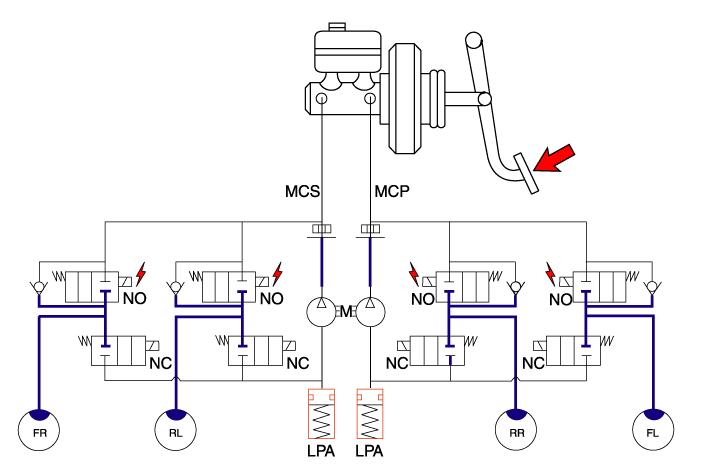
| 3. | Hold Mode When the brake fluid pressure is maximally decreased in wheel cylinder, HECU sends a signal to solenoid valve to keep the fluid pressure, voltage is supplied to inlet valve but it is not supplied to outlet valve. At this time inlet and outlet valves are closed and brake fluid is kept in wheel cylinder.
|
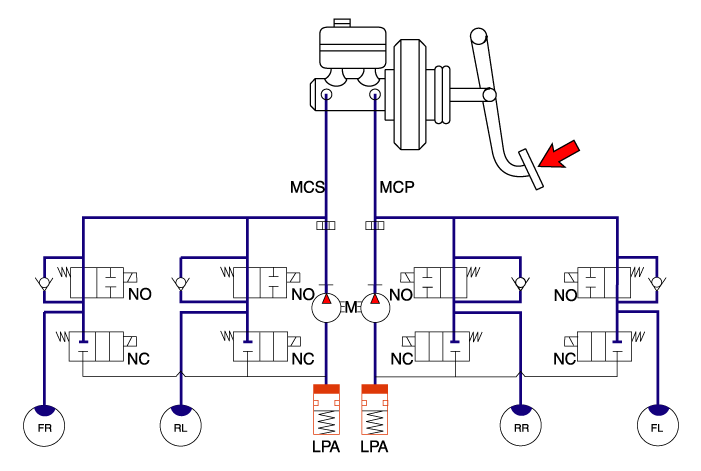
| 4. | Increase Mode If HECU determines there's no lock-up in the wheel, HECU cuts voltage to solenoid valve. So voltage is not supplied to each solenoid valve, brake fluid passes through the inlet valve to wheel cylinder, resulting in pressure increase.
|
ABS HECU External Diagram
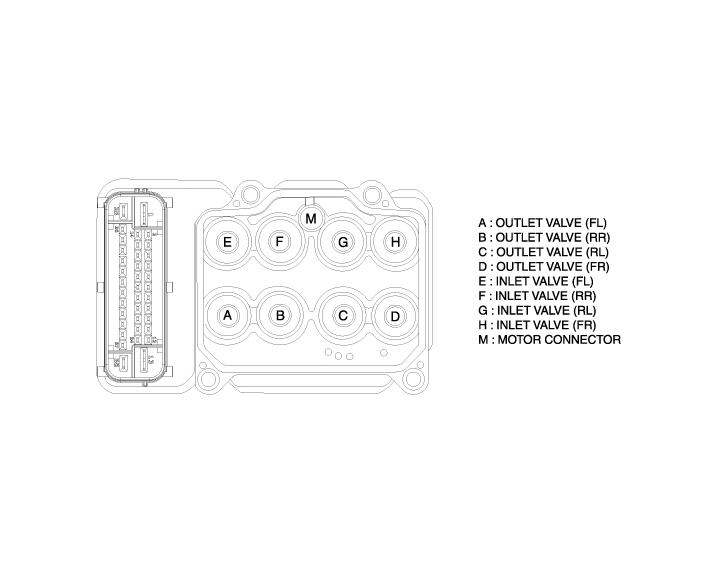
Hydraulic System Diagram
 Components and components location
Components and components location
Components1. ABS control module (HECU)2. Front wheel speed sensor3. Rear wheel speed sensor4. ESC OFF switch..
Other information:
Hyundai Elantra (CN7) 2021-2025 Owner's Manual: Transmission ranges
The indicator in the instrument cluster displays the shift lever position when the ignition switch is in the ON position. P (Park) Always come to a complete stop before shifting into P (Park). To shift from P (Park), you must depress firmly on the brake pedal and make sure your foot is off the accelerator pedal. If you have done all of the above and still cannot shift the lever out of P (Pa..
Hyundai Elantra (CN7) 2021-2025 Service Manual: Schematic diagrams
Schematic Diagram1. Air cleaner2. Delivery pipe & injector3. Engine4. Purge control solenoid valve (PCSV)5. Fuel tank air filter6. Fuel pump7. Fuel filler neck8. Fuel filler cap9. Fuel tankCanisterCanister is filled with charcoal and absorbs evaporated vapor in fuel tank. The gathered fuel vapor in canister is drawn into the intake manifold by the ECM/PCM when appropriate conditions are set.Pu..
Copyright © 2025 www.helantra7.com